Legislation
Workplace Health and Safety Regulations
N.S. Reg. 52/2013
Part 1 INTERPRETATION AND APPLICATION
Section 1.10 Manufacturer’s specifications and standards for equipment and components
1.10 (1) Except as otherwise provided in these regulations, an employer must
(a) ensure that any equipment, components of equipment or components of a system are erected, installed, assembled, used, handled, stored, adjusted, maintained, repaired, inspected, serviced, tested, cleaned and dismantled in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications for the equipment, components or system; and
(b) comply with and ensure compliance with the applicable standards for the equipment, components or system as specified in these regulations.
(2) Except as otherwise provided in these regulations, a person must use equipment, components of equipment or components of a system in accordance with
(a) the manufacturer’s specifications for the equipment, components or system; and
(b) any applicable standards for the equipment, components or system specified in these regulations.
Section 1.11 Engineer’s certification required for other use of equipment or components
1.11 (1) An employer must obtain a written certification from an engineer in accordance with subsection (2) that certifies that the employer’s intended use of equipment, components of equipment or components of a system provides an adequate level of safety for all persons at or near the workplace in all of the following circumstances:
(a) the employer intends to use the equipment, components of equipment or components of a system for a purpose or in a manner that is
(i) not specifically permitted by the manufacturer’s specifications,
(ii) not specifically permitted by an applicable standard referred to in these regulations;
(b) the employer intends to use equipment, components of equipment or components of a system for which no manufacturer’s specifications exist or are provided.
(2) An engineer must do all of the following before certifying equipment, components of equipment or components of a system under subsection (1):
(a) ensure that the use of the equipment, components of equipment or components of a system as intended by the employer is in accordance with generally accepted engineering practices;
(b) identify, as part of the written certification, any measures to be taken to provide an adequate level of safety.
(3) An engineer must sign any written certification they prepare under this Section.
Section 1.12 Inspection and re-certification of equipment
1.12 (1) An employer must ensure that any equipment used is inspected
(a) by the user, before each use; and
(b) by a competent person, annually, or more frequently as specified in any applicable Part of these regulations.
(2) An employer must ensure that any manufacturer’s specifications that provide instructions on how to conduct an inspection under subsection (1) are followed.
(3) An employer must ensure that used equipment is re-certified in accordance with 1 of the following:
(a) the manufacturer’s specifications;
(b) an engineer’s certification, if an engineer’s certification was obtained under Section 1.11.
(4) A person must perform any inspections required by this Section and as specified in any applicable Part of these regulations.
Section 1.13 Equipment protected from damage or exposure
1.13 An employer must ensure that equipment that may be exposed to heat, abrasion or corrosion is either
(a) made of material that is able to withstand the exposure without being damaged; or
(b) protected from the exposure.
Section 1.14 Taking equipment out of service
1.14 (1) An employer must ensure that equipment is taken out of service if any of the following apply:
(a) the equipment is defective;
(b) the equipment has come into contact with
(i) excessive heat, or
(ii) a chemical or other substance that may corrode or otherwise damage the equipment or a component of the equipment;
(c) for fall-protection and rope access equipment, the equipment has been used to stop a fall.
(2) A person must not use any equipment described in subsection (1).
(3) An employer must ensure that equipment that is taken out of service under subsection (1) is not returned to service until it is inspected, repaired as necessary and re-certified by
(a) the manufacturer; or
(b) if certification by the manufacturer is not possible or reasonably practicable, an engineer.
(4) The following must be done for equipment that is taken out of service:
(a) if the equipment is awaiting inspection, repair or re-certification, it must be
(i) immediately removed from the work area,
(ii) clearly identified as taken out of service, and
(iii) stored separately from equipment that has not been taken out of service;
(b) if the equipment is not awaiting inspection, repair or re-certification, it must be destroyed immediately.
Section 1.16 Emergency services agencies exemptions for fall protection and rope access work
1.16 An employer who is an emergency services agency is not required to establish a specific written fall-protection safe-work plan or rope access safe-work plan for a specific work area when responding to an emergency if they
(a) have established the following applicable procedures for the work:
(i) a fall protection safe-work procedure under Section 21.3,
(ii) a code of practice for rope access work under Section 22.5; and
(b) they train to and comply with the procedures in clause (a) and standard protocols for emergency services work applicable to a work area where a person is at a risk of falling.
Part 21 FALL PROTECTION
Section 21.1 Definitions for Part 21
21.1 In this Part,
“arborist” means a person trained and employed, in whole or in part, to climb trees for an economic or scientific purpose, including any of the following:
(i) detecting and treating disease, infections or infestations,
(ii) pruning, spraying or trimming,
(iii) repairing damaged trees,
(iv) assessing growth or harvesting potential;
“body belt” means a body support device that encircles the body at or about the waist;
“energy absorber” means a component of a fall-protection system consisting of a device that dissipates kinetic energy and does not return it to the fall-arrest system or into a person’s body;
“fall distance” means the vertical distance a person may fall, measured from the surface where the weight of a person is supported to the surface the person could fall onto;
“fall-arrest system” means a fall-protection system consisting of an assembly of components that arrests a person’s fall when properly assembled, used together and connected to a suitable anchorage;
“fall-protection system” means any secondary system that is intended to prevent a person from falling or arrests a fall that occurs, and includes guardrails, temporary flooring, travel-restraint systems, personnel safety nets and fall-arrest systems;
“full-body harness” means a body-holding device, similar to a parachute harness, that transfers suspension forces or impacts during a fall arrest to a person’s pelvis or skeleton;
“guardrail” means a fall-protection system consisting of vertical and horizontal members that
(i) are capable of withstanding concentrated forces, as prescribed in these regulations or an applicable standard,
(ii) warn of a fall hazard, and
(iii) reduce the risk of a fall;
“horizontal lifeline” means a flexible line made from wire, fibre rope, wire rope, or rod, with end terminations at both ends, that extends horizontally from one end anchorage to another;
“lanyard” means a flexible line or strap used to secure a full-body harness to an energy absorber, fall-arrester, lifeline or anchorage;
“lifeline” means a component of a fall-protection system consisting of a vertical lifeline or a horizontal lifeline;
“personnel safety net” means a fall-protection system that uses at least 1 net to stop a person who is falling before the person makes contact with a lower level or obstruction;
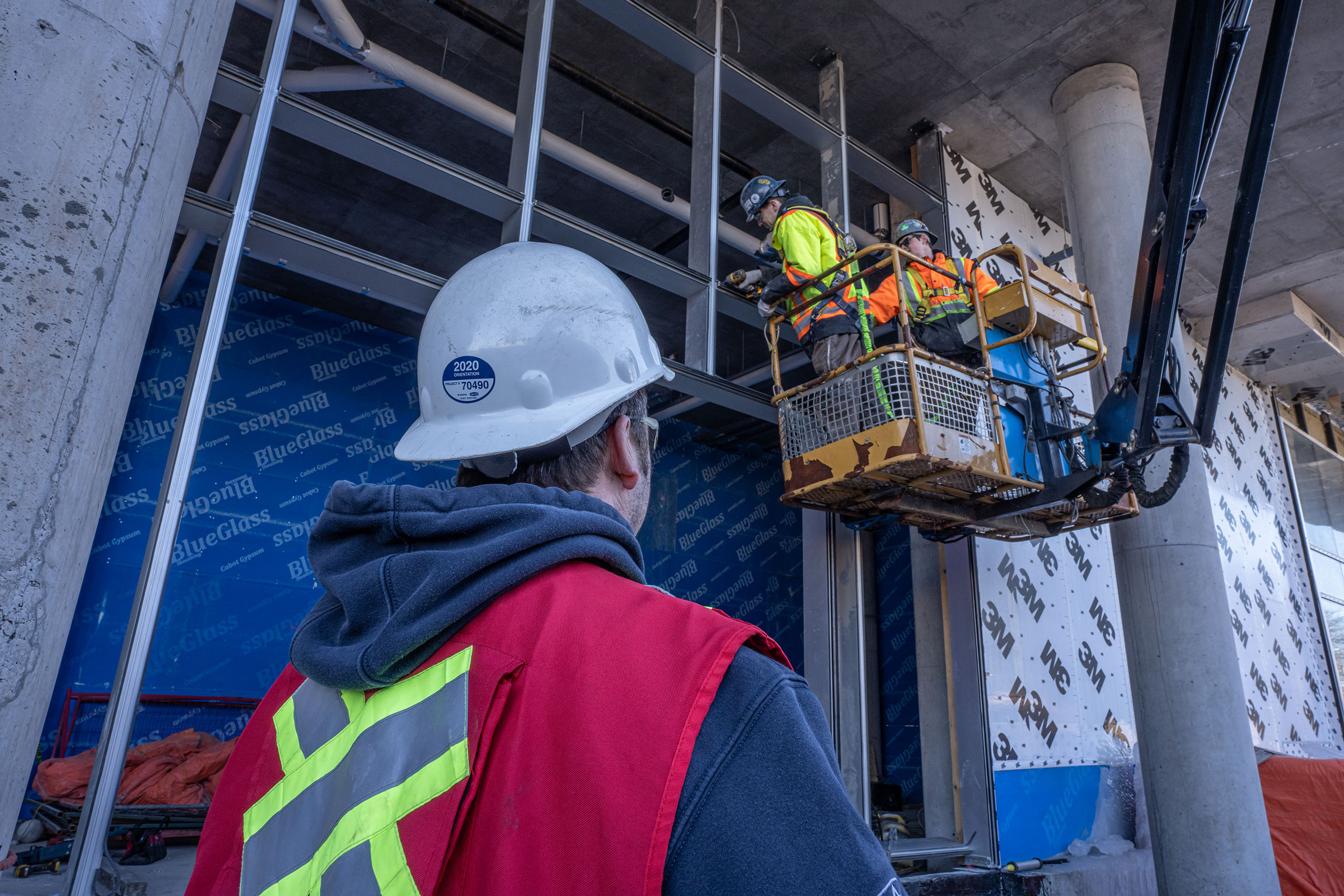
“elevating work-platform” means a mobile horizontal working surface that provides access and support to a person at a workplace, and that is elevated and lowered by means of a mechanism that complies with Part 23: Scaffolds and Other Elevated Work-platforms;
“safe surface” means an area that meets all of the following criteria:
(i) it is large enough and strong enough to adequately support a person who falls,
(ii) it is level enough to prevent a further fall by a person who has fallen,
“self-retracting device” means a device that arrests a person’s fall by performing a tethering function while allowing vertical movement below the device to the maximum working length of the device;
“temporary flooring” means a fall-protection system consisting of a horizontal working surface that is designed, constructed and installed to provide access to areas that do not have permanent flooring by protecting a person from falling through an unprotected opening;
“travel restraint system” means a fall-protection system that will prevent a person from reaching an unprotected edge or opening;
“vertical lifeline” means a flexible lifeline with an end termination on the top end that is connected to an anchorage or anchorage connector and hangs vertically from where it is connected;
“work-platform” means a raised temporary horizontal working surface that provides access and support to a person at a workplace;
“work-positioning system” means an assembly of components that, when properly assembled and used together, supports a person in a position or location so that the person’s hands are free in the work position, but does not include a boatswain’s chair, ladder, rope access or scaffold.
Section 21.2 Fall protection required
21.2 (1) Except as provided in subsections (3) to (5), fall protection is required if a person is at risk of falling from a work area where the fall distance is
(a) 3 m or more above the nearest safe surface or water;
(b) less than 3 m and the work area is above 1 of the following:
(i) a surface or thing that could cause injury to the person on contact that is worse than an injury from landing on a solid, flat surface,
(ii) exposed hazardous material, such as in an open tank, pit or vat.
(2) If fall protection is required, an employer must ensure that at least 1 of the following means of fall protection is used, as appropriate in the circumstances:
(a) a guardrail;
(b) temporary flooring;
(c) a personnel safety net;
(d) a travel restraint system;
(e) a fall-arrest system.
(3) Fall protection is not required for a person who is entering or exiting a work area by a safe means of access and egress.
(4) Fall protection is required only where reasonably practicable and to the extent reasonably practicable in any of the following circumstances:
(a) if work must be performed on or from a vehicle, rail car or other mobile equipment;
(b) if it is not reasonably practicable to perform work other than from a ladder and it is not reasonably practicable for the person performing the work to maintain adequate contact with the ladder while performing the work;
(c) if the density of tree branches prevents an arborist from crotching.
(5) If it is not reasonably practicable to use fall protection in the circumstances described in subsection (4), an employer must ensure that an alternate control measure is used to reduce, to the extent reasonably practicable, the risk of a fall.
Section 21.3 Written fall-protection safe-work procedure
21.3 (1) Except as provided in subsection (2), an employer must establish a written fall-protection safe-work procedure for the type of work to be performed in any work area where fall protection is required and the maximum fall distance is less than 7.5 m.
(2) A written fall-protection safe-work procedure is not required under subsection (1) if any of the following conditions apply:
(a) all persons performing the work are protected by a permanent guardrail;
(b) the work is performed from a work-platform described in Sections 23.12 to 23.15 of Part 23: Scaffolds and Other Elevated Work-platforms and all persons performing the work are using adequate fall protection.
(3) A fall-protection safe-work procedure must be based on a hazard assessment of the work typically performed by the employer and must include all of the following information:
(a) the nature of the work to be performed;
(b) the typical duration of the work;
(c) a description of the work;
(d) a list of the primary tools or equipment used in the work;
(e) reference to applicable health and safety legislation and regulations;
(f) a list of potential fall hazards of the work and their associated risks;
(g) the risk controls to be used to prevent injury to persons coming in contact with known hazards;
(h) the effect of weather conditions;
(i) the name of the person or position that has supervisory responsibility for the work, whether the person is present at the work area or not;
(j) the training and qualifications required for persons who will perform the work, as determined by the employer;
(k) a method for communicating the fall-protection safe-work procedure to any person who may be affected by the procedure.
Section 21.4 Written fall-protection safe-work plan
21.4 (1) Except as provided in subsection (2), an employer must establish a specific written fall-protection safe-work plan for a specific work area where fall protection is required and the fall distance is 7.5 m or more.
(2) A specific written fall-protection safe-work plan is not required under subsection (1) if any of the following conditions apply:
(a) all persons performing the work are protected by a permanent guardrail;
(b) the work is performed from a work-platform described in Sections 23.12 to 23.15 of Part 23: Scaffolds and Other Elevated Work-platforms and all persons performing the work are using adequate fall protection;
(c) the work is performed by an emergency services agency in accordance with Section 1.16.
(3) A fall-protection safe-work plan must be established based on a hazard assessment of the specific work to be performed in the work area and must include all of the following information:
(a) the nature of the work to be performed;
(b) the anticipated duration of the work;
(c) a description of the work;
(d) a list of the primary tools or equipment to be used in the work;
(e) reference to applicable health and safety legislation and regulations;
(f) a list of potential fall hazards of the work and their associated risks;
(g) the fall-protection system or systems to be used at the work area;
(h) any anchorages to be used during the work;
(i) if a fall-arrest system is to be used, confirmation that the clearance distances below the work area are sufficient to prevent a person from striking
(i) the nearest safe surface or water,
(ii) a surface or thing that could cause injury to the person on contact, or
(iii) exposed hazardous material, such as an open tank, pit or vat;
(j) a procedure to address the risks associated with the potential for swing as a result of anchorage placement when a person is using a fall-arrest system;
(k) the procedures to be used to assemble, maintain, inspect, use and disassemble a fall-protection system, as applicable;
(l) schedules for inspecting any fall-protection systems and the names of any persons responsible for carrying out the inspections;
(m) adequate written rescue procedures to be used if a person falls and requires rescue, including if a person is suspended by a fall-arrest system or personnel safety net;
(n) the effect of weather conditions;
(o) the name of a designated competent person to supervise the work area;
(p) the training and qualifications required for persons who will perform the work, as determined by the employer;
(q) a method for communicating the fall-protection safe-work plan to any person who may be affected by the plan.
(4) If a workplace has more than 1 work area for which a fall-protection safe-work plan is required, an employer may create a separate plan for each specific work area or one overall plan for the workplace that includes all of the requirements necessary for each specific plan.
Section 21.5 Guardrails
21.5 (1) An employer must ensure that a guardrail that is used as a means of fall protection is installed at all of the following places in a work area:
(a) around any uncovered opening in any surface;
(b) at the perimeter or other open side of a work area.
(2) A guardrail must be designed and installed in compliance with the latest version of CSA standard CSA 797 , “Code of Practice for Access Scaffolds”.
(3) If there is a risk of falling at a doorway or the opening of a building floor, roof, walls or shaft, an employer must ensure that a guardrail is
(a) installed in accordance with this Section; and
(b) marked with a warning sign that indicates the presence of a doorway or other opening.
Section 21.6 Temporary flooring
21.6 An employer must ensure that temporary flooring that is used as a means of fall protection is able to withstand 4 times the maximum load likely to be on it and is installed so that it meets all of the following:
(a) it extends over the entire work area with the exception of any openings necessary for the carrying out of work;
(b) it is securely fastened to prevent lateral and upward movement.
Section 21.7 Personnel safety nets
21.7 (1) An employer must ensure that a personnel safety net used as a means of fall protection is designed, manufactured, installed, used, inspected, tested and made of materials in accordance with the latest version of ANSI standard A10.11, “American National Standard for Construction and Demolition Operations – Personnel and Debris Nets”.
(2) Despite any requirements set out in the standard required by subsection (1), a personnel safety net must be erected and installed in accordance with all of the following:
(a) it must be erected and installed under the supervision of a competent person;
(b) it must be positioned as close as reasonably practicable, but no more than 9 m below the work area and extend at least 2.4 m on all sides beyond the work area;
(c) it must be positioned and maintained so that when arresting the fall of a person, the maximum deflection of the personnel safety net does not permit any portion of the person to contact another surface;
(d) it must be free of debris, obstructions or intervening objects that may be struck by a person who falls from a workplace into the net.
Section 21.8 Travel restraint systems
21.8 An employer must ensure that a personal travel restraint system that is used as a means of fall protection to restrict movement meets the requirements of the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.16 , “Design of active fall-protection systems”.
Section 21.9 Fall-arrest systems
21.9 An employer must ensure that a fall-arrest system that is used as a means of fall-protection is erected, installed, assembled, used, handled, stored, adjusted, maintained, repaired, inspected, serviced, tested, cleaned and dismantled in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications and designed in accordance with the requirements of the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.16 , “Design of active fall-protection systems”.
Section 21.10 Fall-arrest for arborists
21.10 (1) An arborist using a fall-arrest system as a means of fall protection must ensure that the fall-arrest system includes all of the following:
(a) a work-positioning system and a travel restraint system, the design, markings and instructions of which comply with the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.1 , “Body Belts and Saddles for Work Positioning and Travel Restraint”;
(b) if reasonably practicable, a second climbing rope or safety strap that is manufactured for the purpose of tree climbing and that meets all of the following criteria:
(i) it provides additional stability,
(ii) it provides back-up fall protection,
(iii) it is capable of withstanding the greater of the following:
(A) 2 times the maximum load likely to be on it,
(B) a load of 22 kN.
(2) An arborist must do all of the following before climbing in a work area:
(a) visually assess the structural stability of the tree;
(b) select and assess the safest path of ascent;
I select an appropriate crotch position as a work area.
(3) While working in a tree with a fall-arrest system, and [an] arborist must do all of the following:
(a) wherever practicable, work from a crotch position with the fall-arrest system secured to an anchorage above the crotch position;
(b) when changing crotch positions, remain secured by the fall-arrest system to the anchorage for the previous crotch position until secured by the fall-arrest system to the anchorage for the next crotch position;
I not change crotch positions without selecting the next crotch position in advance;
I* ensure that slack only occurs in ropes or lines that are part of the fall-arrest system, if it is
(i) essential to the performance of the work, and
(ii) no greater than is consistent with the safe performance of the work;
(d)* not climb above an anchorage unless secured by another fall-arrest system secured at or above the level of the arborist;
(g)* not work in crews of fewer than 2;
(h)* have at least 1 crew member remain on the ground at the work area;
(f)* when transferring from an elevating work-platform to a tree, remain attached to an anchorage on the work-platform by way of a fall-arrest system until secured to an anchorage on the tree by way of a fall-arrest system.
[*Clause lettering as in original.]
Section 21.11 Work-positioning systems
21.11 (1) Unless otherwise prescribed in these regulations, an employer must ensure a work-positioning system is used in combination with a fall-arrest system in all of the following circumstances:
(a) the centre of gravity of the person using the work-positioning system extends beyond the edge from which a person could fall;
(b) the state or condition of the work surface creates a slipping or tripping hazard.
(2) A person must not use, and an employer must ensure a person does not use, a work-positioning system as a means of fall arrest.
Section 21.12 Full-body harnesses
21.12 An employer must ensure that a person who is using a personal fall-arrest system wears a full-body harness and that the full-body harness is used and certified in compliance with the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.10 , “Full Body Harnesses”.
Section 21.13 Body belts
21.13 (1) An employer must ensure that the design, markings and instructions of body belts used comply with the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.1 , “Body Belts and Saddles for Work Positioning and Travel Restraint”.
(2) An employer must ensure that body belts are not used as a component of a fall-arrest system.
(3) A person must not use a body belt as a component of a fall-arrest system.
Section 21.14 Energy absorbers and lanyards
21.14 (1) An employer must ensure that a lanyard or an energy absorber used in a fall-arrest system is used and certified in compliance with the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.11 , “Energy Absorbers and Lanyards”.
(2) An employer must ensure that a lanyard used in a fall-arrest system is equipped with an energy absorber, unless all of the following conditions are met:
(a) the combined free-fall distance and the energy absorber deceleration distance exceed the distance between the work area and a safe surface or hazard;
(b) the fall-arrest system is designed by a competent person to limit the free fall to less than 1.22 m and 8 kN arresting force;
(c) the fall-arrest system does not permit the user to contact an unsafe surface.
Section 21.15 Anchorages
21.15 An employer must ensure that all anchorages used as components of a fall-protection system are capable of withstanding the following forces in any direction in which the force may be applied:
(a) 22 kN, for non-engineered anchorage;
(b) 2 times the maximum arresting force anticipated, for an engineered anchorage.
Section 21.16 Horizontal and vertical lifelines
21.16 (1) An employer must ensure that a horizontal lifeline used as a component of a fall-protection system meets all of the following:
(a) it is designed and installed in compliance with the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.16 , “Design of Active Fall-Protection Systems;
(b) it is used, certified and made of material in compliance with the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.13 , “Flexible Horizontal Lifeline Systems”.
(2) An employer must ensure that a vertical lifeline used as a component of a fall-protection system is used and certified in accordance with the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.2.1, “Fall Arresters, Vertical Lifelines and Rails”.
Section 21.17 Self-retracting devices
21.17 (1) An employer must ensure the design, markings and instructions for a self-retracting device used as a component of a personal fall-arrest system comply with the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.2.2 , “Self-Retracting Devices for Personal Fall-Arrest Systems”.
(2) An employer must ensure a self-retracting device used as a component of a fall-protection system is
(a) anchored above the user’s head unless the manufacturer’s specifications allow using a different anchorage location; and
(b) used in a manner that
(i) minimizes the hazards of swinging, and
(ii) if the user falls, limits the distance they drop during the swing to 1.2 m.
Section 21.18 Connecting components
21.18 (1) An employer must ensure all connecting components for a fall-arrest system are used and certified in compliance with the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z259.12 , “Connecting Components for Personal Fall-Arrest Systems (PFAS)”.
(2) An employer must ensure any carabiners and snap hooks used as components of a fall-arrest system are
(a) self-closing and self-locking; and
(b) only capable of being opened by a minimum of 2 consecutive and deliberate manual actions.
(3) An employer must ensure that each component of a fall-protection system is compatible with all of the following, as indicated in the manufacturer’s specifications and instructions for use of their equipment:
(a) each other component and that the safe function of any component does not interfere with the safe function of another component;
(b) the work conditions and conditions of the physical environment under which the equipment is to be used.
Section 21.19 Fall-protection training required
21.19 (1) An employer must ensure that a person takes and successfully completes training on fall protection at all of the following times:
(a) before they do any of the following:
(i) use fall protection,
(ii) work in, supervise or plan the work for a work area where fall protection is required; and
(b) once at least every 3 years.
(2) A person must not use fall protection or work in, supervise or plan the work for a work area where fall protection is required before successfully completing training as required by this Section.
(3) In order to successfully complete training, a person must be deemed competent to inspect and use fall protection by 1 of the following persons who conducted the training:
(a) their employer;
(b) a training organization.
(4) Training must be instructed by a competent person.
(5) The person conducting the training must identify a method of evaluating the person taking the training and determining whether a person successfully completes the training.
Section 21.20 Fall-protection training topics
21.20 Training on fall protection must include all of the following, as applicable to the nature of the work:
(a) a review of all applicable health and safety legislation, regulations and standards;
(b) identification of fall hazards;
(c) a review of the hierarchy of controls that may be used to eliminate or minimize risk of injury from a fall;
(d) the different methods of fall protection and the most suitable application of the methods;
(e) fall-protection and safe-work procedures;
(f) instruction on assessing and selecting specific anchors that may be used for various applications;
(g) instruction on selecting and correctly using fall-protection components, including connecting hardware;
(h) information about the effect of a fall on the human body, including all of the following:
(i) free fall,
(ii) swing fall,
(iii) maximum arresting force, and
(iv) the purpose of energy absorbers,
(i) pre-use inspections of equipment and systems;
(j) emergency response procedures to be used if a fall occurs;
(k) practice in all of the following:
(i) inspecting, fitting, adjusting and connecting fall-protection systems and components,
(ii) the emergency response procedures required by clause (j).
Section 21.21 Record of fall-protection training
21.21 (1) A record of fall-protection training required under Section 21.19 for each participant who successfully completes the training must be maintained by all of the following:
(a) the employer;
(b) any training organization that conducts the training.
(2) A record of training under this Section must include all the following information:
(a) the name of the participant;
(b) the date or dates of training;
(c) the name of the instructor;
(d) the name of the employer;
(e) the name of the training organization, if training is not conducted by the employer;
(f) a description of the training;
(g) the expiry date before which training must be renewed.
(3) Each person who takes fall-protection training required by Section 21.19 must be given a copy of their record maintained under this Section.
Section 21.22 Fall-protection training certificate or card
21.22 (1) A person who conducts training must give each person who successfully completes the fallprotection training required by Section 21.20 a training certificate or card, signed by the instructor, with all of the following clearly indicated on it:
(a) the name of the participant;
(b) the date or dates of training;
(c) the name of the employer and the training organization, if training is not conducted by the employer;
(d) the type of training;
(e) the expiry date for the training certificate or card before which training must be renewed.
(2) A person must have their fall-protection training certificate or card available at the workplace at all times.
Part 23 SCAFFOLDS AND OTHER ELEVATED WORK-PLATFORMS
Section 23.13 Elevating work-platforms
23.13 (1) An employer must ensure that portable, self-propelled and self-propelled boom-supported elevating work-platforms are designed, constructed, erected, maintained, inspected, monitored and used in accordance with the latest version of the following applicable standards:
(a) CSA standard CSA B354.1 , “Portable Elevating Work Platforms”;
(b) CSA standard CSA B354.2 , “Self-Propelled Elevating Work Platforms”;
(c) CSA standard CSA B354.4 , “Self-Propelled, Boom-Supported Elevating Work Platforms”;
(d) CSA standard CSA C225 , “Vehicle Mounted Aerial Devices”.
(2) An employer must ensure that elevating work-platforms used for fire-fighting are designed, constructed, erected, maintained, inspected, monitored and used in accordance with the latest version of the following applicable standards:
(a) NFPA standard NFPA 1901, “Standard for Automotive Fire Apparatus”;
(b) NFPA standard NFPA 1911, “Standard for the Inspection, Maintenance, Testing and Retirement of In Service Automotive Fire Apparatus”.
(3) An employer must ensure that a record of inspections, tests, repairs, modifications and maintenance activities required by the applicable standards in subsections (1) and (2) includes the name and signature of the person or persons who performed the required activities.
(4) Whether or not guardrails are also installed, before operating the equipment in subsection (1) or (2), an employer must ensure, in accordance with Part 21: Fall Protection, that fall-arrest equipment is worn and anchored to a suitable anchorage.
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY ACT
S.N.S. 1996, c. 7
Section 3
- In this Act,
(a) “aggrieved person” means an employer, constructor, contractor, employee, self-employed person, owner, supplier, provider of an occupational health or safety service, architect, engineer or union at a workplace who is directly affected by an order or decision;
(b) “analyst” means a person appointed as an analyst by the Minister pursuant to this Act;
(c) “Board” means the Labour Board established under the Labour Board Act;
(d) “committee” means a joint occupational health and safety committee established pursuant to this Act;
(e) “compliance notice” means a response, in writing, to an order of an officer, describing the extent to which the person against whom the order was made has complied with each item identified in the order;
(f) “constructor” means a person who contracts for work on a project or who undertakes work on a project himself or herself;
(g) “contractor” means a person who contracts for work to be performed at the premises of the person contracting to have the work performed, but does not include a dependent contractor or a constructor;
(h) “contracts for work” includes contracting to perform work and contracting to have work performed;
(i) “Council” means the Occupational Health and Safety Advisory Council established pursuant to this Act;
(j) “dependent contractor” means a person, whether or not employed under a contract of employment and whether or not furnishing the person’s own tools, vehicles, equipment, machinery, material or any other thing, who performs work or services for another on such terms and conditions that the person is
(i) in a position of economic dependence upon the other,
(ii) under an obligation to perform duties mainly for the other, and
(iii) in a relationship with the other more closely resembling that of an employee than an independent contractor;
(k) “Deputy Minister of Labour and Advanced Education” includes a person designated by the Deputy Minister of Labour and Advanced Education to act in the stead of the Deputy Minister;
(l) “Director” means the Executive Director of Occupational Health and Safety or any person designated by the Executive Director pursuant to this Act to act on behalf of the Executive Director;
(m) “Director of Labour Standards” means the Director of Labour Standards under the Labour Standards Code;
(n) “Division” means the Occupational Health and Safety Division of the Department of Labour and Advanced Education;
(o) “employee” means a person who is employed to do work and includes a dependent contractor;
(p) “employer” means a person who employs one or more employees or contracts for the services of one or more employees, and includes a constructor, contractor or subcontractor;
(q) “former Act” means Chapter 320 of the Revised Statutes, 1989, the Occupational Health and Safety Act;
(r) Repealed. [S.N.S. 2010, c. 37, s. 117]
(s) “Minister” means the Minister of Labour and Advanced Education;
(t) “occupation” means any employment, business, calling or pursuit;
(u) “officer” means an occupational health and safety officer appointed pursuant to this Act and includes the Director;
(v) “owner” includes a trustee, receiver, mortgagee in possession, tenant, lessee or occupier of lands or premises used as a workplace and a person who acts for, or on behalf of, an owner as an agent or delegate;
(w) “police officer” means
(i) a member of the Royal Canadian Mounted Police, or
(ii) a member or chief officer of a police force appointed pursuant to the Police Act;
(x) “policy” means an occupational health and safety policy made pursuant to this Act;
(y) “practicable” means possible, given current knowledge, technology and invention;
(z) “program” means an occupational health and safety program required pursuant to this Act, unless the context otherwise requires;
(aa) “project” means a construction project, and includes
(i) the construction, erection, excavation, renovation, repair, alteration or demolition of any structure, building, tunnel or work and the preparatory work of land clearing or earth moving, and
(ii) work of any nature or kind designated by the Director as a project;
(ab) “reasonably practicable” means practicable unless the person on whom a duty is placed can show that there is a gross disproportion between the benefit of the duty and the cost, in time, trouble and money, of the measures to secure the duty;
(ac) “regularly employed” includes seasonal employment with a predictably recurring period of employment that exceeds four weeks, unless otherwise established by regulation or ordered by an officer;
(aca) “repeatedly” means occurring more than once within the preceding three year period;
(ad) “representative” means a health and safety representative selected pursuant to this Act;
(ae) “self-employed person” means a person who is engaged in an occupation on that person’s own behalf and includes a person or persons operating a sole proprietorship but does not include a dependent contractor;
(aea) “serious injury” means an injury that endangers life or causes permanent injury;
(af) “supplier” means a person who manufactures, supplies, sells, leases, distributes or installs any tool, equipment, machine or device or any biological, chemical or physical agent to be used at or near a workplace;
(ag) “union” includes a trade union as defined in the Trade Union Act that has the status of bargaining agent under that Act in respect of any bargaining unit at a workplace, and includes an organization representing employees where the organization has exclusive bargaining rights under any other Act in respect of the employees;
(ah) “workplace” means any place where an employee or a self-employed person is or is likely to be engaged in any occupation and includes any vehicle or mobile equipment used or likely to be used by an employee or a self-employed person in an occupation.
[S.N.S. 2000, c. 28, s. 86; 2010, c. 66, s. 2; 2010, c. 37, s. 117; 2011, c. 24, s. 2; 2016, c. 14, s. 1]
Section 63
- (1) The employer shall notify the Director
(a) as soon as possible, but in no case later than twenty-four hours, after a fire, flood or accident at the workplace that causes
(i) unconsciousness,
(ii) a fracture of the skull, spine, pelvis, arm, leg, ankle, wrist or a major part of the hand or foot,
(iii) loss or amputation of a leg, arm, hand, foot, finger or toe,
(iv) a third degree burn to any part of the body,
(v) loss of sight in one or both eyes,
(vi) asphyxiation or poisoning,
(vii) any injury that requires the admission to hospital, or
(viii) any injury that endangers the life,
of an employee, unless the injury can be treated by immediate first aid or medical treatment and the person can return to work the following day;
(b) as soon as possible, but in no case later than twentyfour hours, after
(i) an accidental explosion,
(ii) a major structural failure or collapse of a building or other structure,
(iii) a major release of a hazardous substance, or
(iv) a fall from a work area in circumstances where fall protection is required by the regulations,
at the workplace, whether any person is injured or not; and
(c) immediately when a person is killed from any cause, or is injured from any cause in a manner likely to prove fatal, at the workplace.
(2) A true copy of the notice of accident required to be given by an employer to the Workers’ Compensation Board, pursuant to the Workers’ Compensation Act , may be delivered to the Director as sufficient notice pursuant to this Section if it is delivered within the time required in subsection (1).
(3) Where notice is required to be sent to the Director pursuant to this Section, the employer shall notify the committee or representative at the workplace, if any.
[S.N.S. 2010, c. 66, s. 12; 2016, c. 14, s. 4]
Occupational Safety General Regulations
N.S. Reg. 44/99
Part 1 Title and Definitions
Section 2 Definitions
- In these regulations,
(a) “Act” means the Occupational Health and Safety Act ;
(aa) “adequate” means sufficient to protect a person from injury or damage to health;
(b) “ALI” means the Automotive Lift Institute;
(ba) “angle of repose” means the angle with the horizontal at which material will no longer flow freely;
(c) “ANSI” means the American National Standards Institute;
(ca) “approved” means approved by the Department or by an agency or authority designated or selected by the Department to make approvals;
(d) “ASME” means the American Society of Mechanical Engineers;
(e) “ASTM” means the American Society for Testing and Materials;
(ea) “CGA” means the Compressed Gas Association;
(f) “CGSB” means the Canadian General Standards Board;
(g) “competent person” means a person who is
(i) qualified because of their knowledge, training and experience to do the assigned work in a manner that ensures the health and safety of every person in the workplace, and
(ii) knowledgeable about the provisions of the Act and regulations that apply to the assigned work, and about potential or actual danger to health or safety associated with the assigned work;
(ga) “compressed air” means air mechanically raised to a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure;
(h) “CSA” means the Canadian Standards Association;
(i) “demolition” means the destruction or removal of all, or part, of an existing building or structure;
(ia) “Department” means the Department of Labour and Advanced Education;
(j) “designated” means, in relation to an employer, appointed in writing by the employer;
(k) “electrical installation” means the wires, machinery, apparatus, appliances, devices, material and equipment used or intended for use for the generation, transmission, distribution, supply and use of electrical power or energy, and includes a power line and power line equipment;
(l) “engineer” means a person who is registered as a member or licensed to practise under the Engineering Profession Act and is competent to do the work being performed;
(m) “firefighter” means
(i) an employee who provides fire suppression services to the public from a fire department within a municipality or local service district, or
(ii) an industrial firefighter;
(n) “guardrail” means a fall protection system consisting of vertical and horizontal members that
(i) are capable of withstanding concentrated forces, as prescribed in these regulations or an applicable standard,
(ii) warn of a fall hazard, and
(iii) reduce the risk of a fall;
(o) “hazardous substance” means chemical or biological material, dangerous goods within the meaning of theDangerous Goods Transportation Act or a controlled product within the meaning of theHazardous Products Act (Canada) that is likely to, because of its harmful nature, cause injury or damage to the health or safety of a person exposed to it;
(p) “hoist” means a device or equipment and its structure used for lifting or lowering material, including cranes, an automotive lift, a winch, a chain fall or other similar device, but does not include a lift truck, a power operated elevating work platform, a device to which the Elevators and Lifts Act applies or a hoist that operates in a shaft in the underground at a mine;
(pa) “ITSDF” means the Industrial Truck Standards Development Foundation;
(q) “industrial firefighter” means an employee who
(i) is designated to fight fires at the employee’s place of employment, and
(ii) is employed by an employer who does not, in the normal course of its business, provide fire suppression services to the public;
(qa) “latest version” means, in relation to a standard or other publication, the latest edition of the standard or publication as supplemented, amended, added to, replaced or superseded;
(r) “lift truck” means a lift truck as defined in the latest version of ANSI standard ANSI/ITSDF B56.1, “Safety Standard for Low Lift and High Lift Trucks”;
(s) “locked out” means to have
(i) isolated the energy source or sources from a machine, equipment, tool or electrical installation,
(ii) dissipated any residual energy in a system, and
(iii) secured the isolation of the energy source or sources by an inhibiting device that is operated by a key or other process,
and to have performed a “lock-out” has a similar meaning;
(t) “machine” Repealed. [N.S. Reg. 52/2000, s. 1]
(u) “manufacturer’s specifications” means
(i) the written instructions of a manufacturer of a machine, material, tool or equipment that outline the manner in which the machine, material, tool or equipment is to be erected, installed, assembled, started, operated, used, handled, stored, stopped, adjusted, carried, maintained, repaired, inspected, serviced, tested, cleaned or dismantled, and
(ii) a manufacturer’s instruction, operating or maintenance manual and drawings respecting a machine, tool or equipment;
(ua) “mobile crane” means a mobile crane to which the latest version of CSA standard CSA Z150 , “Safety Code on Mobile Cranes” applies;
(v) “NFPA” means the National Fire Protection Association;
(va) “overhead crane” means any mechanical device or structure that is used to raise, lower and move material that travels overhead and that incorporates a
(i) power driven drum, bridge and cable or rope,
(ii) single or multiple girder, and
(iii) moveable bridge carrying a moveable or fixed hoisting mechanism,
but does not include wall cranes, cantilever gantry cranes and semi-gantry cranes;
(vb) “personal flotation device” means personal protective equipment that is capable of supporting a person with their head above water without the direct effort of the person wearing the equipment;
(w) “power line” means the above-ground or underground wiring that is used to distribute electricity;
(x) “power line equipment” means the components that are required to distribute electricity by means of a power line;
(y) “power operated elevating work platform” means a mobile horizontal working surface that provides access and support to a person at a workplace, and that is elevated and lowered by means of a mechanism and [that complies with] Part 23: Scaffolds and Other Elevated Work Platforms, of the Workplace Health and Safety Regulations made under the Act, including a standard listed in subsection (4) thereof;
(z) “powered mobile equipment” means self-propelled equipment that is designed to operate on land in conditions other than a public highway, but does not include equipment primarily designed to transport persons, a lift truck or a power operated elevating work platform;
(aa) “SAE” means the Society of Automotive Engineers;
(ab) “structural fire-fighting” means the activities of rescue, fire suppression and conservation of property from fires involving buildings, structures, vehicles, vessels, aircraft or other large objects constructed by human effort;
(ac) “surface mine” means a work or undertaking, other than a trench, for the purpose of opening up, proving, removing or extracting any metallic or non-metallic mineral or mineral bearing substance, rock, earth, clay, sand or gravel by means of an open excavation, and includes a pit or quarry;
(ad) “tower crane” means any mechanical device or structure that
(i) incorporates a power-driven drum and cable or rope and a vertical mast or tower and a jib,
(ii) is of the traveling, fixed or climbing type, and
(iii) is used exclusively for raising, lowering and moving material;
(ae)”trench” means an excavation in which the excavation depth exceeds the excavation width;
(af) “work area” means a location at the workplace at which an employee or self-employed person is or is likely to be working;
(ag) “worked” means drilled, blasted, extracted, excavated, loaded or subjected to other similar work.
[N.S. Reg. 52/2000, s. 1; 151/2003; 53/2013, ss. 1, 93]